PaperLab Turns Useless Trash Into Fresh Sheets Of Paper
The enduring universal appeal of paper lies in its simplicity as a communication tool. Information on the highly portable and always convenient medium of paper is easy to read, easy to digest, and easy to remember. The world has been relaying on paper for communication from the beginning of time. From writing letters to using it for advertisement paper is used everywhere.
Paper is created by using pulpwood logs which is extracted from forest. These tree are chopped and used for making papers for us. Worldwide consumption of paper has risen by 400% in the past 40 years leading to increase in deforestation, with 35% of harvested trees being used for paper manufacture. Paper waste accounts for up to 40% of total waste produced each year. Conventional bleaching of wood pulp using elemental chlorine produces and releases into the environment large amounts of dioxins which are highly toxic, and effects on humans include reproductive, developmental, immune and hormonal problems. They are known to be carcinogenic.
The effect of paper manufacturing can no longer be ignored. To counter this situation Epson, a Japanese electronics company and one of the world’s largest manufacturers of computer printers have come up with the idea of “Paperlab”.
Paperlab:
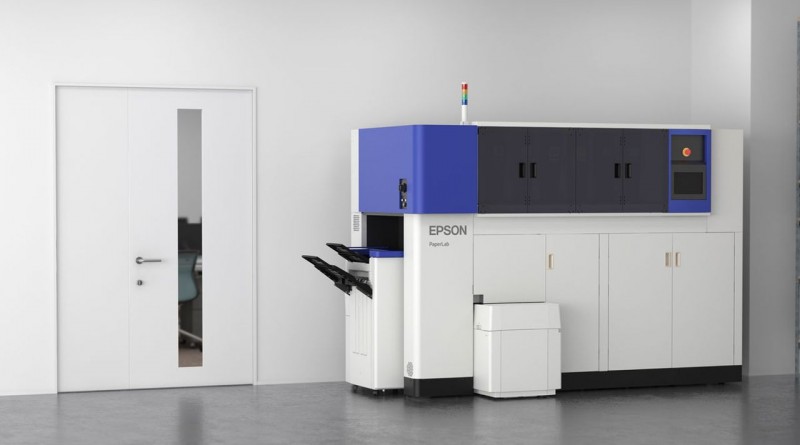
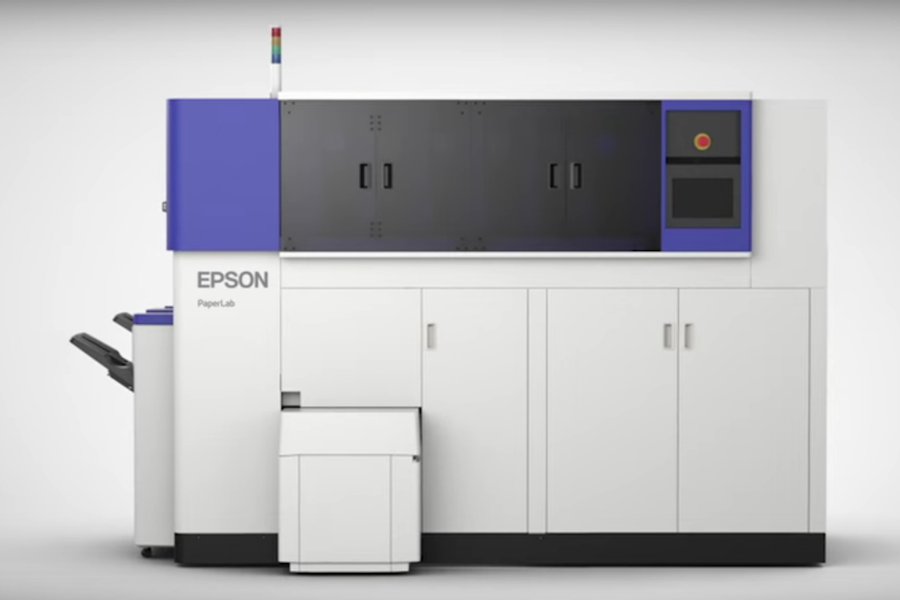
Seiko Epson Corporation has developed what it believes to be the world’s first compact office paper making system capable of producing new paper from securely shredded waste paper without the use of water. Epson has been deeply involved with paper used for its printer products. With this in mind, the company set out to develop technology that would change the paper cycle. With PaperLab, Epson aims to give new value to paper and stimulate recycling.
How Does it work?
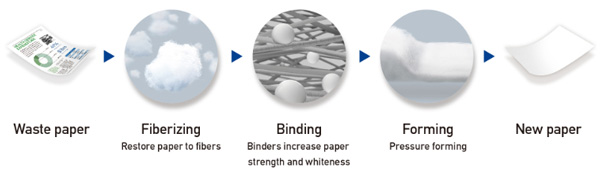
Epson has a foundation of compact, energy-saving and high-precision technologies which enables them to achieve small, energy-efficient products that offer outstanding accuracy and performance. the consumer, office, commercial and industrial sectors, Epson has an immense storehouse of ink and media expertise with it’s printer business operations spanning, as well as the ability to produce reliable, durable systems that operates stably. Epson has developed Dry Fiber Technology without water, a new group of technologies for the PaperLab. Dry Fiber Technology consists of three separate technologies: fiberizing, binding, and forming.
-
Fiberizing:
Paperlab uses an original mechanism where waste paper is transformed into long, thin cottony, fibers. This process immediately and completely destroys confidential documents without using water and its compact size makes it easy to use and store.
-
Binding:
In paperlab a variety of different binders can be added to the fiberized material to increase the binding strength or whiteness of the paper or to add color, fragrance, flame resistance, or other properties needed for a given application.
-
Forming:
With paperlab users can produce sheets of A4 or A3 office paper and even paper for business cards due to forming technology that allows them to control the density, thickness, and size of paper.
Paperlab’s Features:
-
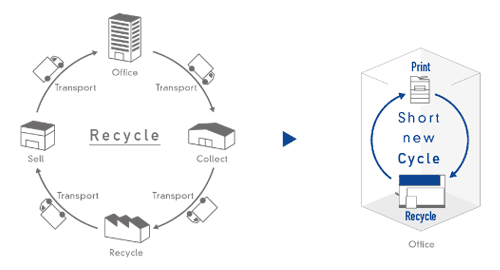
Office-Based Recycling Process:
Papers are recycled in an extensive process that typically involves transporting waste paper from the office to a recycling facility. With the help of PaperLab, Epson is looking to shorten and localize a new recycling process within the office itself.
-
High-speed Production Of Various Types Of Paper:
PaperLab produces the first new sheet of paper within three minutes of having loaded it with waste paper and pressing the Start button. The system is able to produce about 14 A4 sheets per minute that’s about 6,720 sheets in an eight-hour day. Users can also produce a variety of types of paper to meet their needs, from A4 and A3 office paper of various thicknesses to paper for business cards, color paper and even scented paper.
-
Secure Destruction Of Confidential Documents:
Till now enterprise used to hire contractors to handle the disposal of confidential documents or had to shred them themselves. With a PaperLab, enterprises will be able to safely dispose of documents onsite instead of handing them to a contractor increasing it’s security. It’s done as PaperLab breaks documents down into paper fibers, so the information on them is completely destroyed.
-
Environmental Performance:
It takes about a cup of water to make a single A4 sheet of paper, but water being a precious global resource, Epson felt a dry process was needed therefore PaperLab makes paper without the use of water. Recycling of paper onsite in the office shrinks and simplifies the recycling loop. Users are expected to purchase less new paper and reduce their transport CO₂ emissions, which directly reduces the deduction in tree chopping.
Future:
A developmental prototype of the PaperLab will be demonstrated at the Epson booth from December 10 to 12 at Eco-Products 2015, an environmental exhibition that will take place at the Tokyo Big Sight. Epson aims to increase operational efficiency by employing PaperLab to convert used paper into new. The company believes that offices of all types will fundamentally change the way they think about paper.
Here is a trailer by the company itself about “PAPERLAB”:
But there’s still a lot of detail missing from Epson’s description like, what happens to all the waste ink or does it need any other reagents to work and most importantly how well does it work, etc. However it certainly is an attractive idea as it cuts down on waste, it’s good for the environment, and depending on the running costs it might as well be a money-saver, too. Epson says it plans to put the PaperLab into commercial production in 2016. We Here at Engineerpal hope for the best.